Simulation and Modelling
It turns out that the optical forces created in by focused light beams are not so simple to calculate especially when dealing with particles on the order of a wavelength in size. We have devised sophisticated numerical methods to calculate these forces and to understand the underlying electrodynamics at play.
We have two publicly available codes for simulating optical tweezers and shaping light using computer controlled holograms.
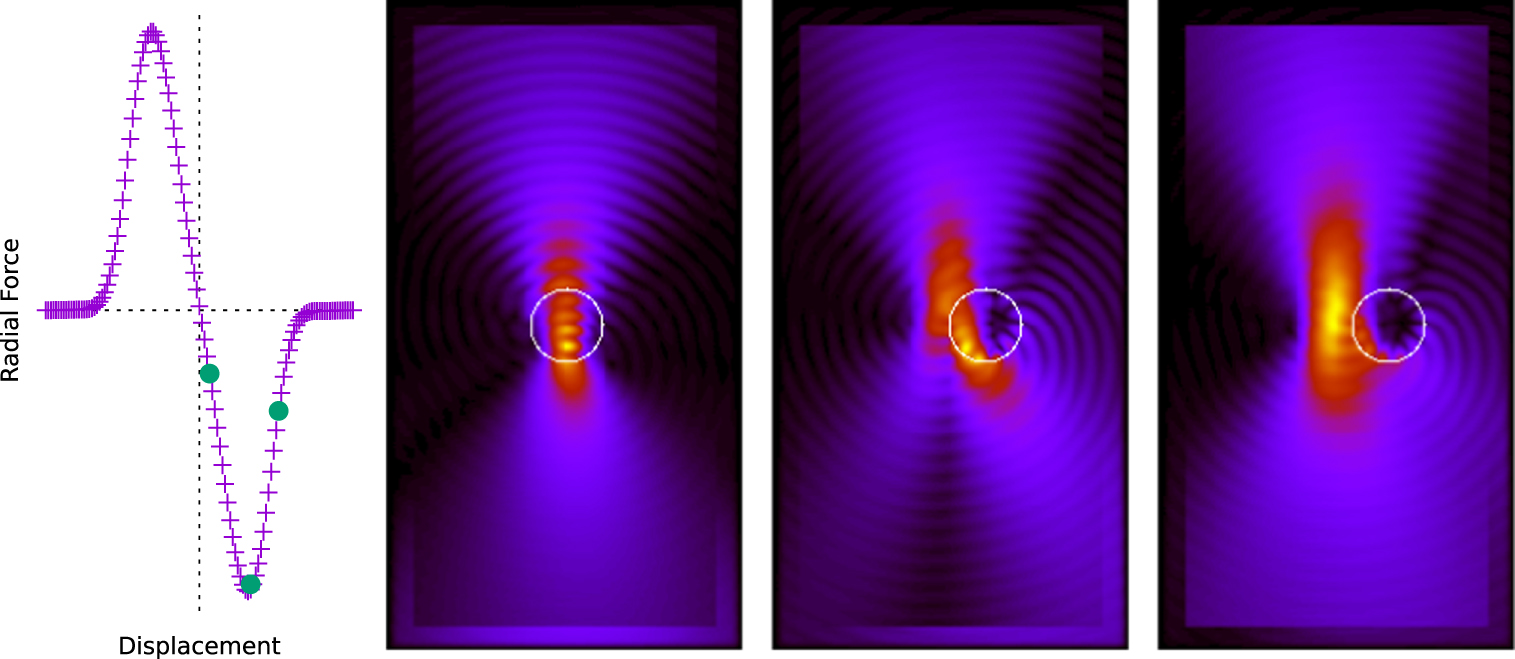
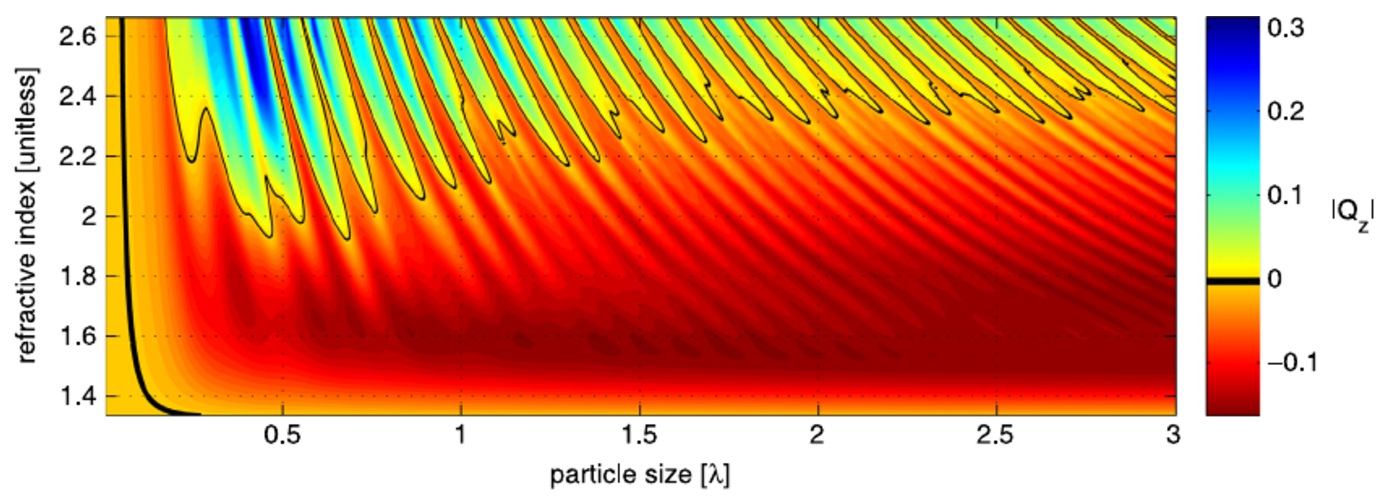
Our previous publications on the topic include:
2017
Active rotational and translational microrheology beyond the linear spring regime
Gibson, L. J., Zhang, S., Stilgoe, A. B., Nieminen, T. A., & Rubinsztein-Dunlop, H. (2017). Physical Review E, 95(4). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.95.042608'
Visual guide to optical tweezers
Lenton, I. C. D., Stilgoe, A. B., Rubinsztein-Dunlop, H., & Nieminen, T. A. (2017). European Journal of Physics, 38(3). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6404/aa6271'
2014
Optical tweezers: Theory and modelling
Nieminen, T. A., Du Preez-Wilkinson, N., Stilgoe, A. B., Loke, V. L. Y., Bui, A. A. M., & Rubinsztein-Dunlop, H. (2014). Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 146, 59–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jqsrt.2014.04.003'
2012
Equilibrium orientations and positions of non-spherical particles in optical traps
Cao, Y., Stilgoe, A. B., Chen, L., Nieminen, T. A., & Rubinsztein-Dunlop, H. (2012). Optics Express, 20(12), 12987. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.20.012987'
2011
T-matrix method for modelling optical tweezers
Nieminen, T. A., Loke, V. L. Y., Stilgoe, A. B., Heckenberg, N. R., & Rubinsztein-Dunlop, H. (2011). Journal of Modern Optics, 58(5-6), 528–544. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500340.2010.528565'
